Introduction
Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) play a crucial role in balancing the supply and demand of power generation, distribution, and consumption. In the face of rising temperatures during summer, energy storage becomes even more important in helping to "reduce peaks" and ensure a stable power supply. This article explores how energy storage can address the challenges posed by high temperatures and mitigate the strain on the electricity grid.
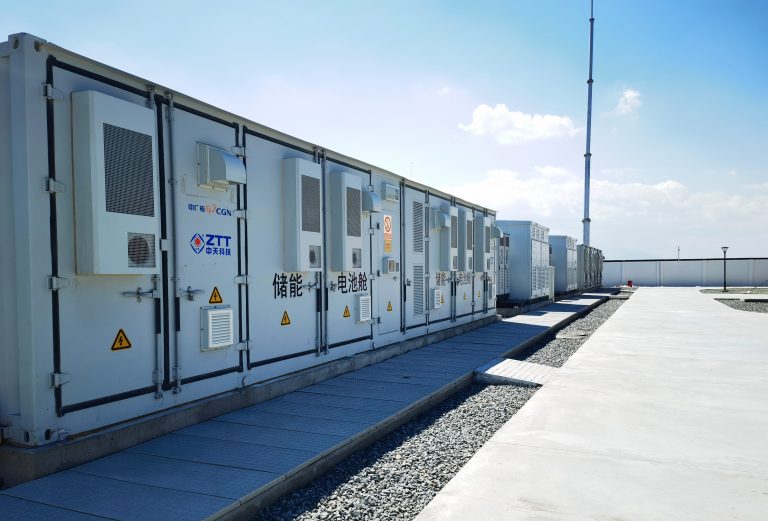

Overview
During periods of low demand, energy storage systems store excess energy generated, which can then be released during times of peak demand. This is particularly relevant during heatwaves when the demand for air conditioners and cooling systems skyrockets, putting immense stress on the electricity grid. To illustrate the urgency of this issue, it's worth noting that several places in China, including Beijing and Tianjin, have recently experienced temperatures of up to 40 ℃. Consequently, the electricity load on the power grid has reached unprecedented levels. The power supply pressure is expected to rise significantly with the arrival of summer. According to the CEC's forecast, the country's peak electricity load is expected to reach around 1.37 billion kilowatts in 2023 under normal weather conditions. This represents an increase of approximately 80 million kilowatts compared to the previous year and up to 100 million kilowatts during prolonged periods of extreme weather.
How to Mitigate Daytime Shortages?
The functions of energy storage are diverse and, from a purely technical point of view, can provide different functions in different application scenarios. The main corresponding functions for short-term power shortages in the grid are peak shaving and demand side response of energy storage.
Currently, power shortages in the grid are dominated by daytime shortages. The current charge and discharge times for new energy, grid, and user-side energy storage are all 2-4 hours, which is an effective means of mitigating daytime shortages.
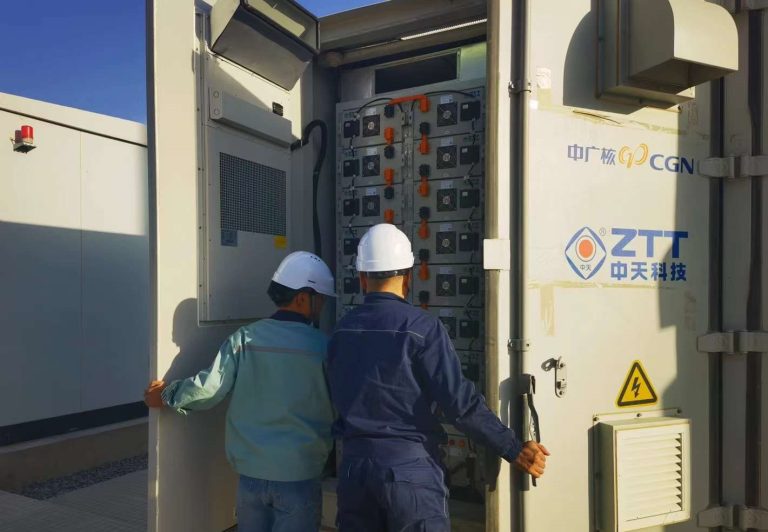

Peaking Applications
New energy side and grid side energy storage are currently based on peaking applications. During power shortages, these systems discharge stored energy in the peaking auxiliary service market or power spot market for peak shaving.
For user-side energy storage, the main profit is currently from the peak-to-valley tariff differential.
Peak Shaving Explained
Peak shaving involves reducing energy demand during periods of high electricity usage, thereby alleviating stress on the power grid and reducing the need to operate expensive and less efficient power plants. For example, energy storage systems can store energy during off-peak hours and discharge this energy during peak demand hours, helping to smooth out electricity demand spikes.
Other functions of energy storage include providing backup power during power outages, helping to integrate renewable energy sources into the grid, and providing frequency regulation services to help maintain grid stability. Additionally, energy storage can improve the efficiency of industrial processes and reduce energy costs through load shifting and other techniques.
About ZTT
ZTT is a trusted solutions provider of Battery Energy Storage Systems and other related products. By harnessing the potential of energy storage, we can effectively address the challenges posed by high temperatures and ensure a reliable and sustainable power supply, even during summer peaks.

> Feel free to contact us for more information: sales@zttcable.com